
Mobile App Localization: A Guide to Boosting Global App Store Growth
Unlock global growth with this guide to mobile app localization. Learn to adapt your app for international markets and boost downloads and conversions.
Thinking of mobile app localization as just a "translation" task is like seeing a rocket ship and calling it a metal tube. It completely misses the point.
In reality, it's one of the most powerful and direct levers you can pull to accelerate user acquisition, boost conversions, and unlock revenue in global markets. Let's be clear: an English-only app strategy is no longer a viable path to scale.
Why Localization Is Your App's Biggest Growth Lever
If you're not localizing, you are intentionally leaving massive growth opportunities on the table. The market data tells a compelling story.
The global mobile app market is projected to skyrocket to USD 1,017.18 billion by 2034, with the Asia Pacific region alone commanding over half of that share. This explosive growth is fueled by billions of users in digital-first economies like China and India who, frankly, expect apps to speak their language.
Connecting Language to Revenue
The connection between language and app store downloads is direct and measurable. It's simple, really. When potential users search the App Store or Google Play, they use keywords in their native language. If your app’s title, description, and screenshots aren't localized, you are simply invisible to them.
This creates a huge barrier to discovery. A user in India is far more likely to download an app presented in Hindi or Tamil, a simple adjustment that could increase adoption by 40% to 50%. By failing to localize, you're not just missing out on users; you're giving your competition a massive, unearned advantage.
Localization isn’t an expense; it’s an investment in market access. For every dollar you spend adapting your app for a new region, you are building a bridge to millions of potential new customers who would otherwise never find you.
From Cost Center to Profit Center
The most successful app developers have already shifted their mindset. They don't see localization as a line item on a budget but as a core part of their user acquisition strategy. It’s a performance marketing channel with a clear ROI that directly boosts app store growth.
Think about the user's journey for a moment:
- Discovery: They search the app store in their native language.
- Evaluation: They scan localized screenshots and read descriptions that resonate with their cultural context.
- Conversion: Feeling understood and confident, they hit the "install" button.
- Retention: They stick around because the in-app experience feels natural and intuitive.
Every single step of this funnel is strengthened by effective mobile app localization. It is the most fundamental way to show international users that your app was built for them, not just translated for them. For a deeper look into the nuances of wording, you might find our article on using "localise" or "localize"" interesting.
When you make your app feel local, you build the trust and familiarity that directly translates into higher conversions and long-term growth.
Laying the Groundwork with Internationalization
Before you even think about translating a single word, you have to get your app's foundation right. This is the engineering groundwork called internationalization, or i18n for short (because there are 18 letters between the 'i' and the 'n').
Think of it like building a house. You wouldn't start picking out paint colors before the plumbing and electrical systems are in place. i18n is that critical infrastructure. It’s the foundational code that makes every future localization effort smooth, scalable, and sane.
Trying to localize an app that hasn't been properly internationalized is a direct path to technical debt and soul-crushing rework. The goal here is to build a single, adaptable codebase that can handle any language, region, or cultural quirk you throw at it, without having to build a new version of the app for every market.
Separate Your Code From Your Content
This is the golden rule of i18n: get all user-facing text out of your code. Every button label, error message, and tooltip needs to be moved into separate resource files. Hardcoding text like "Sign Up" directly into your UI is a classic mistake that makes translation impossible without a developer rewriting the code.
Instead, you replace that hardcoded text with a key, a simple identifier. Your code then uses that key to pull the right string from a language-specific file, all based on the user's device settings.
- For iOS (Swift): You’ll use something like
NSLocalizedString("signup_button_title", comment: "Label for the main sign up button"). This points to an entry in your.stringsfile. - For Android (Kotlin/XML): You reference strings from your
strings.xmlfile with@string/signup_button_title. Each language gets its ownstrings.xmlfile inside a specific folder (likevalues-es/for Spanish).
This separation is the bedrock of an efficient workflow. It means you can hand off the resource files to translators, and they can do their work without ever needing to see, touch, or understand a single line of your application’s source code.
A well-internationalized app creates a clean handoff between developers and linguists. The devs build a flexible container, and the linguists fill it with culturally spot-on content. This parallel workflow is how you launch in new markets fast.
Design for Flexibility, Not Pixels
Here's a hard truth: languages don't care about your pixel-perfect UI. A neat little English phrase can balloon in length when translated to German or shrink when converted to Japanese. A UI built with fixed-width buttons or rigid containers is guaranteed to break.
For example, "Account Settings" (16 characters) becomes "Kontoeinstellungen" (19 characters) in German. That's a 20% increase in length that will cause text to wrap weirdly, overflow its container, or just get cut off. It looks sloppy and unprofessional.
To sidestep this mess, your design and development teams have to build adaptive layouts from day one.
- Ditch fixed pixel values. Use constraints and dynamic sizing that allow elements to grow and shrink.
- Make sure UI elements like buttons and text fields can expand to fit their content gracefully.
- Run tests with "pseudo-localization." This process automatically replaces your text with longer, accented characters (e.g., "Account Settings" becomes "[Àççôûñţ Šéţţîñĝš !!]") to instantly reveal where your UI will crack under pressure.
Prepare for More Than Just Words
Great internationalization goes way beyond text. Your app needs to be ready to handle all sorts of different cultural conventions for displaying data.
- Dates and Times: A user in the U.S. sees dates as
MM/DD/YYYY. A user in the UK expectsDD/MM/YYYY. Don't try to code this logic yourself; use the built-in system libraries that format dates automatically based on the user's locale. - Numbers and Currencies: The number "one thousand twenty-five and fifty cents" is written as
1,025.50in the US, but as1.025,50in Germany. Again, let the native formatting libraries do the heavy lifting for decimal separators, grouping, and currency symbols. - Pluralization: This one trips up a lot of teams. English is simple: we have a singular form ("1 item") and a plural form ("2 items"). But Polish has three or four plural forms depending on the number, and Arabic has six. Hardcoding a simple
if (count > 1)check will completely fail in most languages. Use the platform-specific tools for this, like Android'spluralsresource or iOS's.stringsdictfiles, which are designed to handle these complex grammatical rules for you.
With the technical groundwork laid, it's time to dive into the actual localization (l10n) process. This is where all that prep work really starts to pay off, letting you build a repeatable workflow for rolling into new markets without reinventing the wheel every single time. A solid process turns what feels like a monumental task into something you can actually manage and scale.
The journey doesn’t kick off with translation, though. It starts with data. Before you decide to localize for Germany or Japan, you need to know if there’s an audience waiting for you. Dive into your App Store Connect and Google Play Console analytics. Look for countries where you see high traffic but your conversion rates are tanking. That's a classic sign that a language barrier is the main thing holding you back.
This flowchart maps out the key stages of a solid localization workflow, from sorting out your code and UI all the way through to handling your final assets.
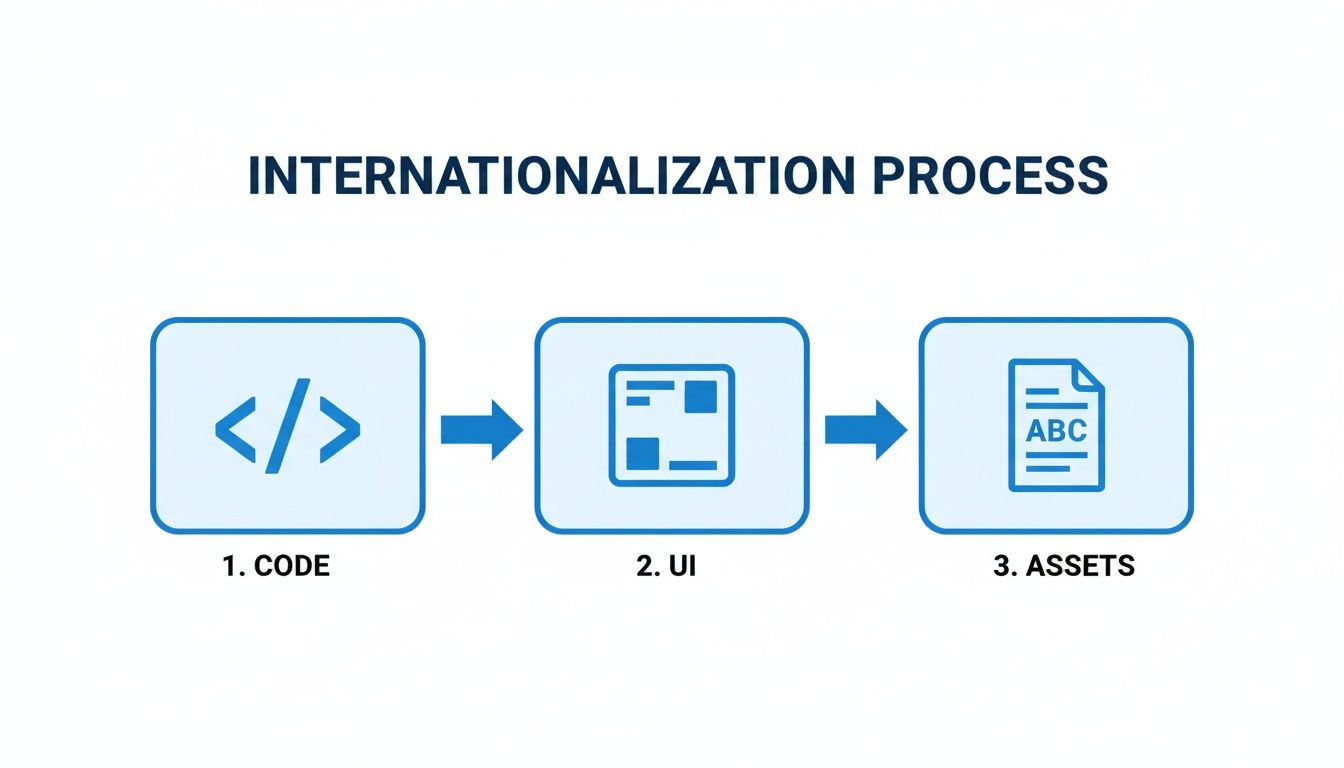
As you can see, a proper workflow moves from the technical prep (code and UI) into content adaptation (assets). This ensures a clean handoff between your development and translation teams, which is critical for staying on schedule.
Choosing Your Translation Strategy
Once you’ve pinpointed your target markets, you need to figure out how you'll get your content translated. You’ve got a few options, each with its own balance of speed, cost, and quality.
Professional Human Translators: This is the gold standard for quality, plain and simple. Professional linguists who are native speakers can capture nuance, cultural context, and brand voice in a way that machines just can't. This is your best bet for the most critical, user-facing content, think app store descriptions, your onboarding flow, and in-app purchase screens.
Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE): This hybrid approach hits a sweet spot. You start with a quick, cheap machine translation from a service like Google Translate or DeepL. Then, a professional human translator comes in to review and polish the output, fixing errors, smoothing out the language, and ensuring it’s culturally appropriate. MTPE is fantastic for less critical text or when you have huge volumes of content to get through.
Machine Translation (MT): Using raw machine translation is definitely the fastest and cheapest route, but it’s loaded with risk. It's really only suitable for internal docs or maybe user-generated content where perfect grammar isn't the priority. For your app's main interface, raw MT can come across as robotic and seriously erode user trust.
Your translation strategy shouldn't be one-size-fits-all. A smart approach is to use a tiered system: professional human translation for your most valuable content (like app store metadata), MTPE for in-app content, and raw MT only where the risks are lowest.
Managing Quality with a TMS
As you start adding more languages, trying to manage string files through email or spreadsheets will quickly descend into chaos. Trust me on this. This is where a Translation Management System (TMS) becomes your best friend. A TMS is the central hub for everything related to your localization efforts.
A TMS automates the whole process of pulling text from your code, sending it off to translators, and then plugging the translated strings right back into your app. The key features you'll rely on are:
- Translation Memory: This is basically a database that saves every sentence you've ever translated. When the same phrase pops up again, the TMS automatically suggests the existing translation. This saves you a ton of time and money, and more importantly, it keeps your language consistent.
- Glossaries: You can build a glossary of key terms, like your brand name or specific feature names, to make sure they’re translated the same way across every single language.
- Collaboration Tools: A TMS gives your developers, translators, and project managers one place to work together. It provides clear version control and communication channels, so everyone is on the same page.
Integrating a TMS creates a reliable system of record for your entire localization operation. It bakes quality control right into your workflow from day one. To see how this kind of groundwork pays off on the store listings, check out our guide on Google Play ASO optimization. By setting up a solid process now, you can confidently scale to dozens of languages without your quality or speed taking a nosedive.
Creating High-Converting Localized App Store Screenshots
Think of your app store listing as your digital storefront. It's often the only shot you get to convince someone to tap that install button, and in a new market, that first impression is everything.
Proper mobile app localization goes way beyond just translating text. You need to create efficient, high-converting app store screenshots and visual assets that feel native, trustworthy, and genuinely compelling to a local audience. This is where your app store creatives become your most powerful tools for boosting conversions.
Screenshots Are More Than Just Translated Text
A common and costly mistake is simply translating the text captions on your English screenshots and calling it a day. What’s compelling in one culture can be confusing or totally irrelevant in another. Real localization means adapting the entire visual story to maximize conversions.
You have to rethink every single element:
- Captions and Callouts: Don't just translate; transcreate. This is all about adapting the marketing message itself. A feature that's a "must-have" in the US might be a "nice-to-have" in Japan, so your callouts need to reflect what local users actually care about.
- UI in Mockups: Show, don't just tell. The user interface inside your device mockups has to be localized, too. Seeing dates, currencies, and text in their own format makes the app feel instantly familiar and removes any hesitation.
- Cultural Imagery: Colors, symbols, and even the people in your screenshots can have wildly different meanings across cultures. A thumbs-up is positive in many Western countries but is a serious insult in parts of the Middle East.
Your app store screenshots aren't just product images; they are localized advertisements. Each one should answer a user's question or solve a problem that is relevant to their specific market, making the decision to download feel obvious and easy.
This is a great example of how different localized app store cards can be tailored with unique illustrations and vibrant colors to appeal to diverse regional tastes.
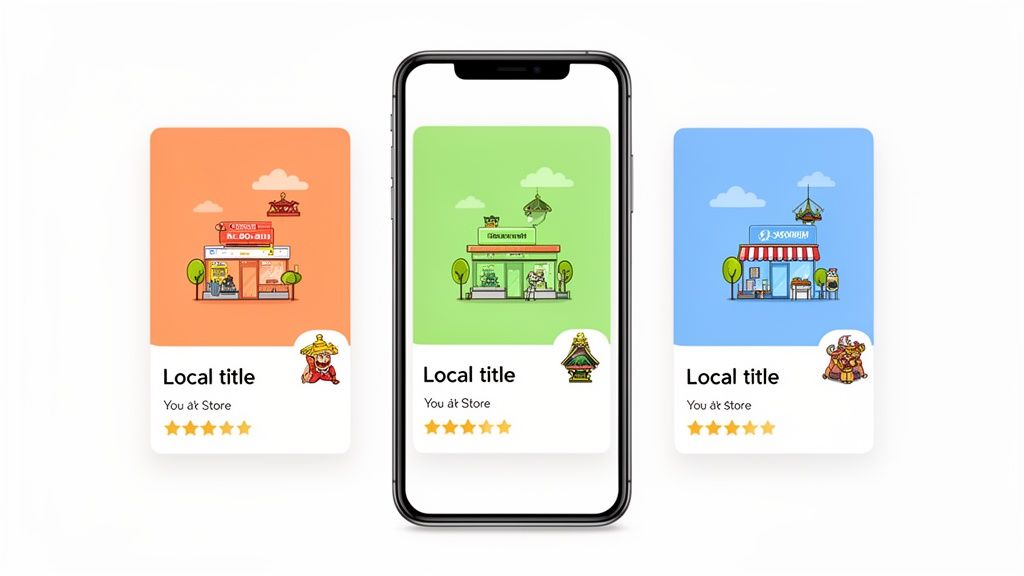
Adapting these visual details shows a deep commitment to the local user experience. It builds trust, and that trust is what dramatically boosts conversion rates.
Automating Visuals for Speed and Scale
Manually creating unique screenshot sets for every language and device is a massive bottleneck. It just doesn't scale. This is where tools designed for app store asset creation become essential for an efficient workflow. For example, using a site editor, you can design a master template with your brand fonts and colors. Then, you can upload a spreadsheet with translated captions for each language and generate a full set of localized screenshots for the Android and iOS stores in minutes.
This approach turns a tedious design task into a scalable workflow. Instead of spending weeks wrestling with a design tool, you can generate a full set of high-converting, culturally relevant screenshots for a new market quickly. If you want to dive deeper, check out our detailed guide on creating the perfect app store mockup.
Nailing Your Metadata for Local Discovery
Great visuals will get people to your page, but they need to be able to find it first. Your app's visibility depends on the text you use in your app store listing, the title, subtitle, and description are critical for App Store Optimization (ASO).
To get those organic installs, you have to optimize this metadata with local keywords. Start by doing keyword research for each target market. Don't just translate your English keywords; you need to dig in and find out what local users are actually searching for.
And don't forget video. A key part of making your app store page appealing is the ability to create multilingual videos for your app preview, which helps your message connect with users in their own language.
It's a tough field to get right; 75% of companies struggle with the technical side of app localization. But the payoff is huge. Localized apps consistently crush their English-only competitors in discovery and revenue.
Just look at a market like China, with 989 million internet users driving 40% of global app spending. In a market that big, localization isn't just a nice-to-have; it's essential for survival. Tailoring your screenshots for popular devices like the iPhone 16 Pro Max or Samsung Galaxy with region-specific copy is a proven way to dramatically increase installs.
By combining culturally adapted visuals with keyword-rich text, you create a powerful, localized store listing that attracts the right users and turns them into loyal customers.
Testing And Launching Your Localized App
You can pour your heart and soul into localizing your app’s UI and store assets, but if you don't stick the landing, none of it matters. A successful global launch isn’t a matter of luck; it’s the direct result of meticulous, almost obsessive, quality assurance.
Skipping this final phase is like building a gorgeous car but never checking if the engine starts. It pretty much guarantees a terrible first impression and can kill your momentum in a new market before you even get off the ground.
A solid QA strategy for a localized app goes way beyond hunting for the usual functional bugs. You have to put on a different hat and look specifically for the unique curveballs that mobile app localization throws at you. This is how you ensure your app doesn't just work correctly but also feels genuinely native to your new international users.
The Two Pillars of Localization QA
When it comes to effective testing, everything really boils down to two distinct but equally vital areas: linguistic and functional validation. You absolutely have to nail both to deliver a polished, professional product. One ensures the words are right; the other makes sure they actually fit.
Linguistic Testing: This is where you get down to the nitty-gritty of the translation quality. Is it accurate? Does it still sound like your brand? Most importantly, is it culturally on-point? A literal translation might be grammatically perfect but come across as clunky, robotic, or even offensive to a native speaker.
Functional Testing: This is all about checking how the localized text plays with your app's UI. Does that notoriously long German word for "Settings" completely wreck your navigation bar? Do right-to-left languages like Arabic render properly without scrambling the entire interface? This is where you catch all those visual and interactive glitches.
Think of it this way: linguistic testing checks if you're speaking the language correctly, while functional testing checks if you're speaking it clearly within the confines of your app's design. Both are essential for creating an experience that feels seamless and trustworthy.
Your Essential QA Checklist
To catch the most common localization bugs, your team needs a structured game plan. And let me be clear: working with native speakers during this phase is non-negotiable. They will spot cultural nuances and linguistic quirks that your internal team, no matter how sharp, will inevitably miss. Their feedback is the difference between an app that is merely translated and one that is truly localized.
To get you started, here’s a practical checklist to guide your QA process.
Localization QA Checklist
A quick rundown of the key areas to review during quality assurance for a localized mobile app.
| Test Area | What to Check | Common Pitfalls |
|---|---|---|
| UI & Layout | Text overflow, truncation (cut-off text), overlapping elements, broken constraints. | Buttons too small for long German words, causing text to wrap awkwardly or get cut off. |
| Cultural Nuances | Appropriateness of colors, icons, images, and cultural references. | Using a hand gesture icon that’s positive in one culture but deeply offensive in another. |
| Data Formatting | Correct display of dates, times, numbers, and currencies for the target locale. | Showing a price as "$10.99" to a user in France who expects to see "10,99 €". |
| Linguistic Accuracy | Grammatical errors, typos, incorrect terminology, and inconsistent tone. | Translating a casual, fun marketing slogan into overly formal, stilted language. |
| Text Directionality | Proper rendering of right-to-left (RTL) scripts like Arabic and Hebrew. | A mirrored UI where text is right-aligned, but icons and buttons stubbornly remain on the left. |
A quick note on bug reporting: for localization testing to be effective, clear communication is everything. The quality of your bug reports directly impacts how quickly developers can find and fix issues. It’s worth taking some time to learn how to write effective bug reports that leave no room for guesswork.
Smart Rollout Strategies for a Smooth Launch
Once your localized app has finally passed QA, resist the urge to do a "big bang" launch across all your new markets at once. That's a recipe for a stressful weekend. A much smarter approach is a phased rollout, which lets you minimize risk and gather real-world data before you go all-in.
Take Google Play's phased release feature, for example. It lets you push the update to a small percentage of users in a specific country first. This is your safety net. You get a chance to monitor for any unexpected crashes or region-specific issues that your internal testing didn't catch. Keep an eye on your analytics, watch for user engagement, and then gradually dial up the rollout percentage as your confidence grows.
Another powerful move is to A/B test your localized app store listings before you even launch. You can test different versions of your icon, screenshots, and descriptions to see which combination actually drives the highest conversion rate in that market. This data-driven approach means your store presence is fully optimized from day one, giving your launch the biggest possible impact.
Common Questions About Mobile App Localization
Diving into app localization can feel a bit overwhelming. There's a lot of new terminology and plenty of forks in the road where a wrong turn can cost you time and money. Let's clear up some of the most common questions that pop up when teams decide to go global.
How Do I Choose Which Languages to Localize First?
Don't just throw a dart at a map. Your best starting point is the data you already have.
Crack open your app store analytics and start hunting for a specific pattern: countries with high traffic but surprisingly low conversion rates. This is almost always a flashing red light signaling a language barrier. You've got interested users finding you, but they're dropping off because the app isn't in their native tongue.
Once you’ve got a shortlist, it's time for some quick market research. For each potential country, look at the smartphone adoption rates and the overall size of the app market. You're looking for the sweet spot: a high-demand market where English proficiency isn't the norm. That's your biggest opportunity.
My advice? Start small and prove the concept.
- Run a pilot: Pick just one to three of your most promising languages to launch first.
- Track everything: Keep a close eye on downloads, engagement, and especially revenue from those specific markets.
- Scale with data: The results from your pilot will tell you exactly where to invest your localization budget next. No guesswork needed.
What's the Difference Between Internationalization and Localization?
This one trips people up all the time, but the analogy I always use is building a house.
Internationalization (i18n) is the architectural blueprint and foundation. It's about designing the house with wiring that can handle any country's voltage and plumbing that can connect to any type of fixture. In the app world, this means engineering your code from day one to handle different languages and regions. You're externalizing text strings, creating flexible UI layouts that don't break with longer words, and making sure your app can handle different date formats and currencies. It's a one-time, upfront engineering effort.
Localization (l10n), on the other hand, is decorating the house for the family moving in. It's painting the walls their favorite color, hanging local art, and stocking the kitchen with familiar foods. For your app, this is the ongoing work of actually translating the text, adapting graphics, and tweaking your app store page for each specific culture.
Internationalization is the technical prep work that makes localization possible. Localization is the continuous cultural adaptation you do for every new market you enter. You can't do the second without the first.
Can I Just Use AI for My Entire App Translation?
Tempting, right? AI-powered machine translation (MT) has come a long way, but going all-in on AI for your user-facing text is a massive gamble.
MT is brilliant for getting a quick first draft or translating internal documents at lightning speed. But it consistently fumbles cultural nuance, brand voice, and context. A purely machine-translated app often feels clunky, cheap, and can instantly erode the trust you've worked so hard to build with your users.
A much smarter, more professional approach is Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE). This hybrid model gets you the best of both worlds. The AI does the initial, heavy-lifting translation, and then a professional human linguist swoops in to review, edit, and polish the output. This ensures your final copy is not only grammatically perfect but also hits the right cultural notes and sounds like your brand.
For the really critical stuff, your app store screenshots, your onboarding flow, your payment screens, don't cut corners. Invest in professional human translators. For generating the text that goes on those screenshots, however, tools with built-in AI translation can be a huge time-saver. You get a scalable starting point that a native speaker can then quickly review and approve.
Ready to create stunning, localized screenshots that boost conversions worldwide? With ScreenshotWhale, you can generate high-quality, on-brand visuals for the App Store and Google Play in minutes. Our AI-powered engine helps you adapt your creatives for over 100 languages, making global launches faster and more effective. Try ScreenshotWhale today.